
Mice were secured into the head coil with a bite bar and the head was taped down to minimize motion. Isoflurane was administered at 1% (mixed with O 2) to keep the respiration rate between 80 and 120 beats per minute (Stafford et al., 2014). We obtained in vivo resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rsfMRI) data from mice using a 7 Tesla Bruker BioSpec (Bruker BioSpin, Billerica, MA) scanner while mice were anesthetized with isoflurane. The aim of this pilot study was to determine whether 5XFAD mice show alterations in brain networks that parallel those observed in patients with AD, including elevated characteristic path length, reduced network efficiency, and decreased hub presence. We compared functional and structural connectomes of 5XFAD transgenic mice with those of nontransgenic controls.
Additionally, studies suggest that AD pathogenesis targets high-traffic hub regions in the brain, spreading from epicenters to secondary networks as the disease progresses (Buckner et al., 2009 Dai et al., 2015 Mallio et al., 2015 Stam et al., 2009 Zhou, Gennatas, Kramer, Miller, & Seeley, 2012 Zhou & Seeley, 2014). These mutations are rare but tend to be associated with aggressive, early onset disease and therefore have provided unique information regarding the pathophysiology of AD (Bateman et al., 2011).Ĭonnectome studies of patients with AD have most consistently demonstrated alterations in measures of network integration and efficiency (Daianu et al., 2013 Fischer, Wolf, Scheurich, Fellgiebel, & Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative, 2015 Kim et al., 2016 Lo et al., 2010 Pereira et al., 2016 Reijmer et al., 2013 Stam, Jones, Nolte, Breakspear, & Scheltens, 2007 Wang et al., 2012 Zhao et al., 2012). However, the only causative factors identified to date are mutations in amyloid precursor protein (APP), presenilin 1 (PSEN1), or presenilin 2 (PSEN2) genes. Risk factors include age, first-degree family history, and the apolipoprotein E (APOE) e4 genotype (Green et al., 2002 Hebert et al., 2010 Saunders et al., 1993 ten Kate et al., 2016 Wolters et al., 2017). There currently are no effective treatments for reversing AD. Over 46 million people have Alzheimer’s dementia globally, and the prevalence is expected to double every 20 years (Prince et al., 2015). Patients with incipient AD initially are cognitively normal, but inevitably progress to severe dementia and death. AD pathology initiates many years before diagnosis and develops slowly in some individuals and more rapidly in others. These preliminary findings suggest that 5XFAD mouse connectomes may provide useful models for investigating the molecular mechanisms of AD pathogenesis and testing the effectiveness of potential treatments.Īlzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common form of age-related neurodegeneration and dementia (Risacher & Saykin, 2013). Hyper-correlation of structural and functional connectivity was observed in transgenic mice compared with nontransgenic controls. Transgenic mice also showed lower small-worldness index in higher structural connectome densities and in weighted structural networks.
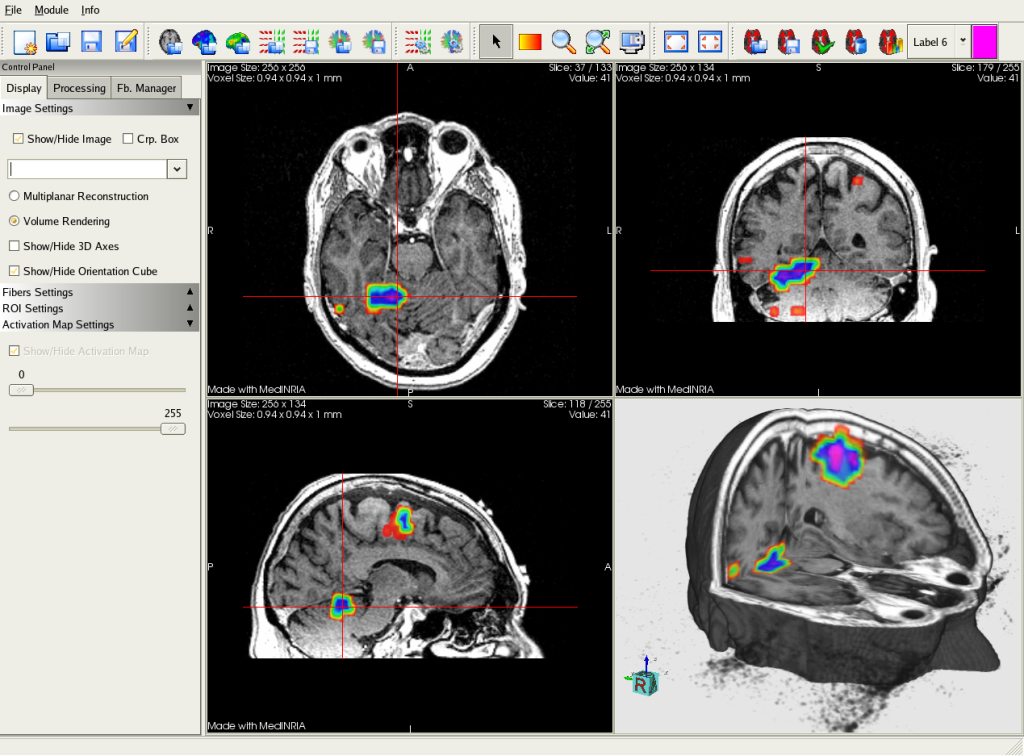
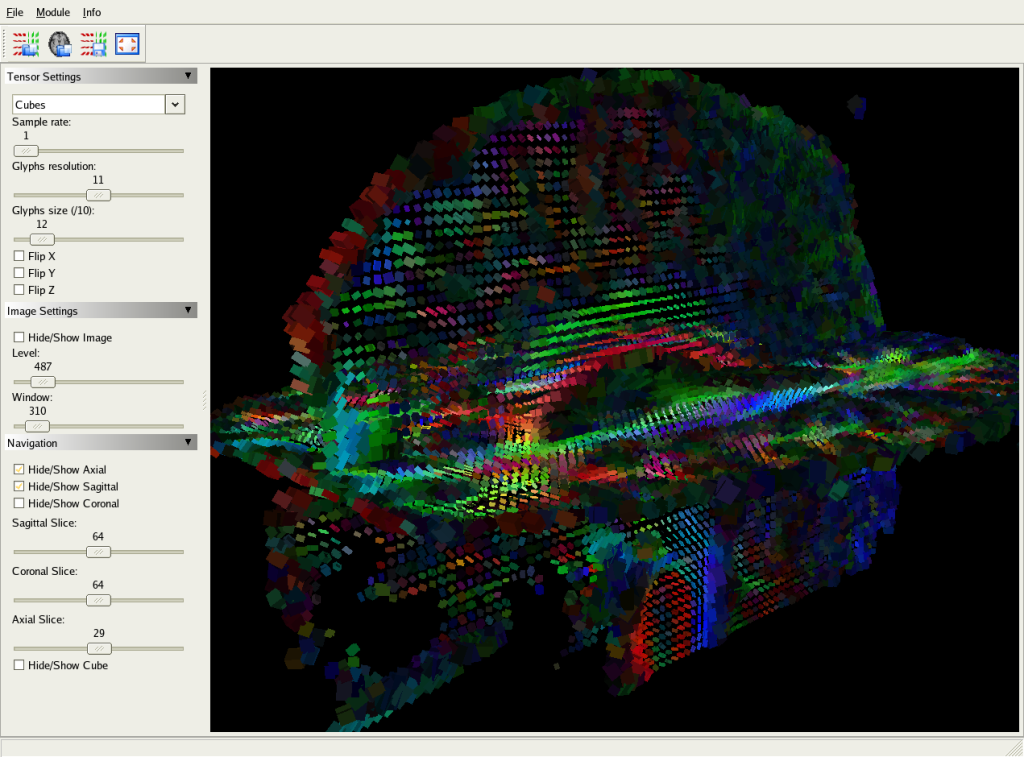
Normalized clustering and modularity were lower in transgenic mice across the upper densities of the structural connectome. Transgenic mice showed higher characteristic path length in weighted structural connectomes and functional connectomes at minimum density. We compared connectome properties between groups using both binarized and weighted networks. We constructed both structural and functional connectomes and measured their topological properties by applying graph theoretical analysis. We obtained diffusion tensor imaging and resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging data for four transgenic and four nontransgenic male mice.

We aimed to determine whether connectome properties of these mice parallel those observed in patients with AD. The five-familial AD (5XFAD) transgenic mouse model exhibits accelerated amyloid-beta deposition, neuronal dysfunction, and cognitive impairment. Neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is associated with amyloid-beta peptide accumulation into insoluble amyloid plaques.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
